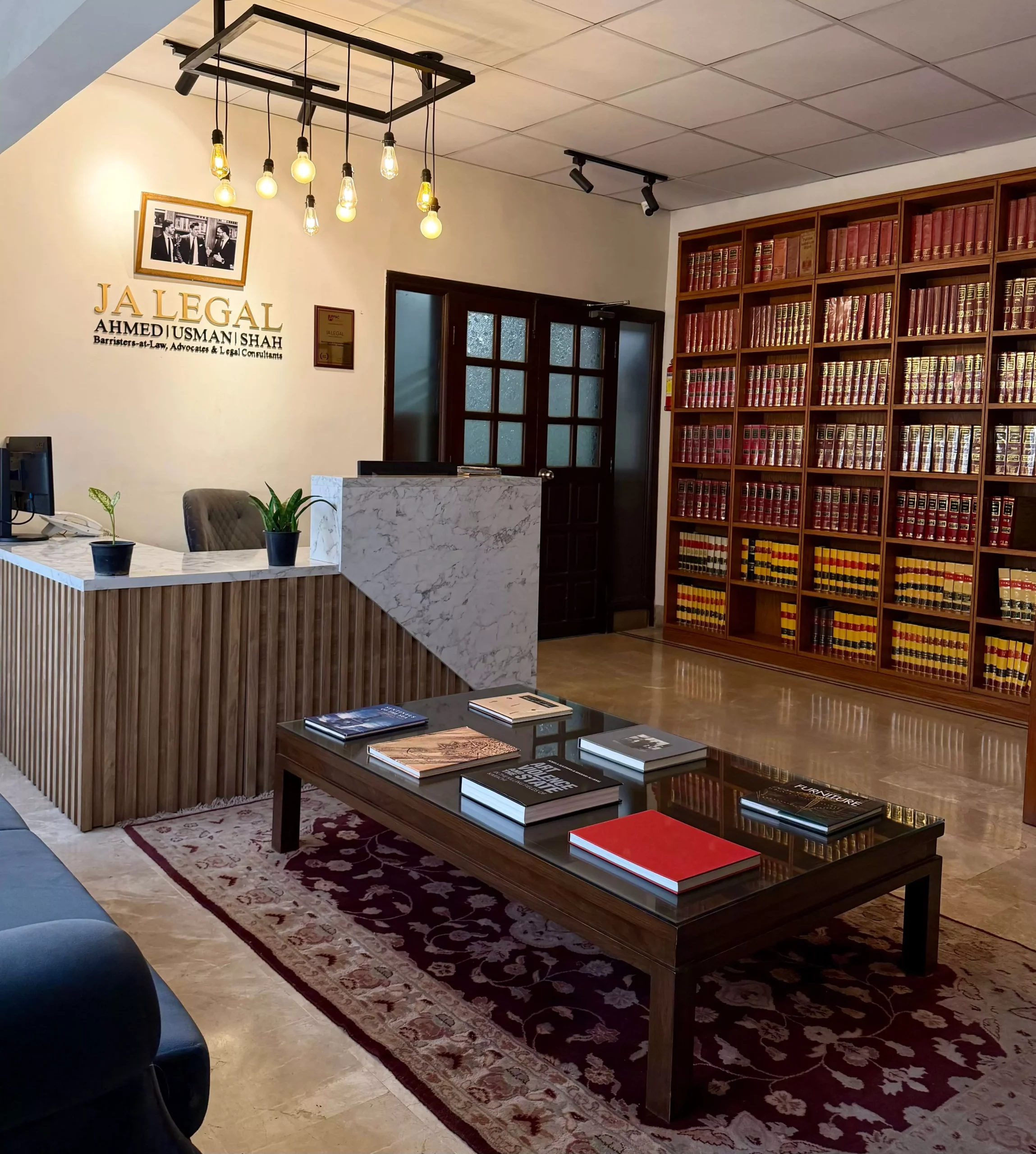
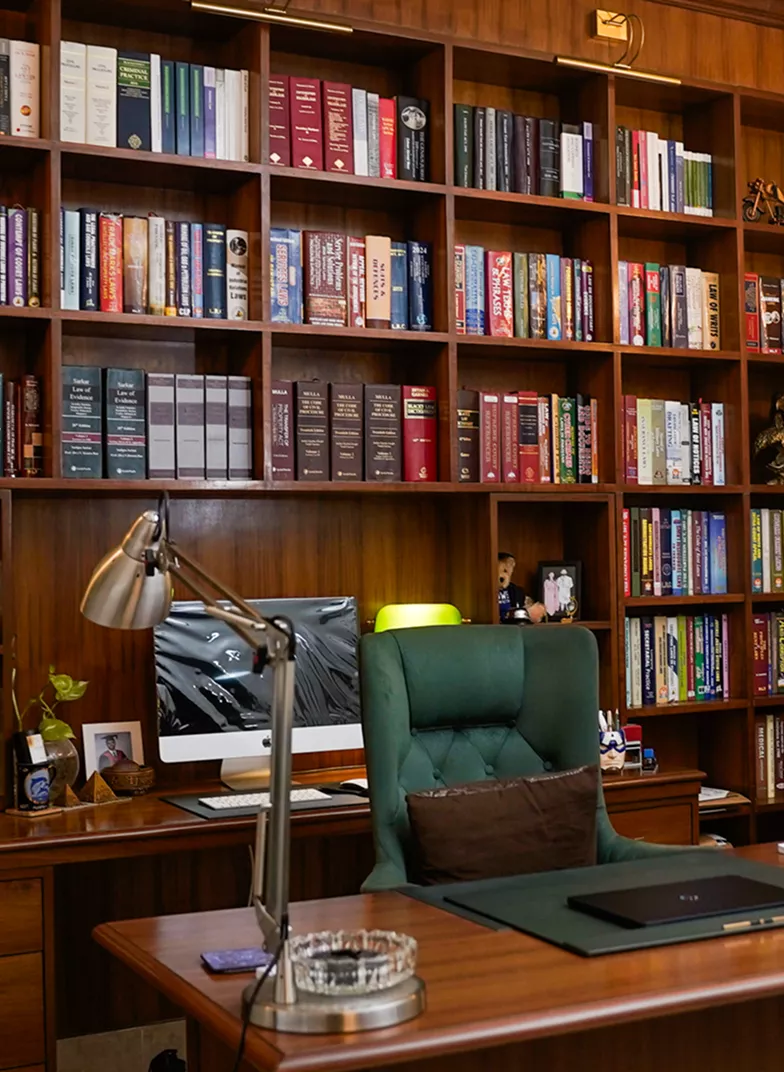
We pride ourselves on delivering exceptional legal services that encompass both contentious and non-contentious matters.
At our firm, we firmly uphold the constitutional right of every individual to seek legal remedies. Our unwavering dedication lies in providing customized legal solutions that precisely meet our clients’ requirements while adhering to the highest professional standards.
Fields Of Expertise
VISION MAKES US WHO WE ARE
Why Choose Us

Deep Expertise
Experienced lawyers offering strategic legal expertise across multiple practice areas.

Personalized Service
Tailored legal guidance focused on your goals and circumstances.

Integrity and Ethics
We uphold the highest standards of honesty, transparency, and professional ethics in every matter.
Latest Updates
we are open for meeting every
working day
 Skip to main content
Skip to main content